
THCA vs Delta 9 THC: Understanding the Differences and Effects
Delta 9-THC vs. THC-A - Everything you need to know

Sara S.
Simple Leaf Staff
There are a number of active cannabinoid compounds in cannabis, and each has been attributed its own set of characteristics. One of these is THCA (aka, Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and the other is Delta 9 THC (aka, Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol). The objective of this article is to help the reader understand the differences between THCA and Delta 9 THC, how they affect us and what their uses might be.
Key Takeaways:
- THCa and THC are very similar but have some distinct differences.
- THCa must undergo a process known as decarboxylation in order to become THC.
- Although research and evidence is still relatively novel, potential uses, applications and benefits of THCa show promise.
What is THCA?
THCA is the molecular precursor of Delta 9 THC, but it lacks the intoxicating effects associated with its psychoactive brother. It’s prevalent in unprocessed, raw freshly harvested cannabis. To transcend into the D9 THC we know and love, it first must be decarboxylated. It’s a chemical process that’s achieved through heating. All of these factors explain further why smoking or vaping cannabis – both of which involve heating through combustion – gets you high.
Key Characteristics of THCA:
- Non-psychoactive in its raw form.
- Found abundantly in fresh cannabis.
- Requires decarboxylation to become psychoactive.

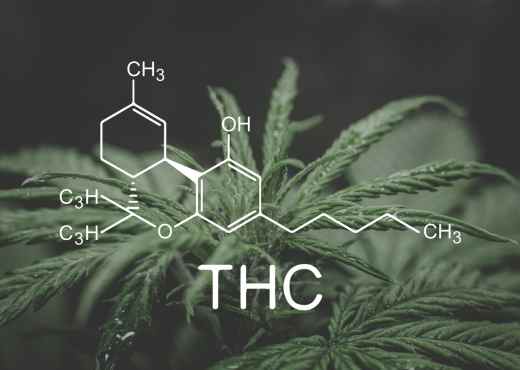
What is Delta 9 THC?
Delta 9 THC is the most famous of the psychoactive compounds in the cannabis plant, and accounts for the ‘high’ associated with cannabis use. Its effect is caused by binding with cannabinoid receptors throughout the mind and nervous system. THC can cause a range of effects, from euphoria to distortions in reality perception.
Key Characteristics of Delta 9 THC:
- Psychoactive, causing the “high” associated with cannabis.
- Produced from THCA through decarboxylation.
- Binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain.
- Used for both recreational and medicinal purposes.
Differences Between THCA and Delta 9 THC
While THCA and Delta 9 THC are closely related, their differences are crucial:
- Psychoactivity: THCA is non-psychoactive, while Delta 9 THC is psychoactive.
- State of Existence: THCA is found in raw cannabis. Whereas Delta 9 THC is produced by heating THCA.
- Effects on the Body: THCA does not bind to the cannabinoid receptors in it’s raw form – unlike its cousin Delta 9 THC – it produces different physiological effects.
Applications and Uses
- THC-A: Often used for its potential therapeutic benefits minus the high and is typically found in the following products: Flower, tinctures, edibles and topicals.
- Delta 9 THC: Most high THC product in which we feel psychoactive effects. Delta 9 is also the primary basis for edibles, oils, and concentrates, while recreational and medicinal uses abound.
Comparing THC-A and Delta 9 THC: Effects and Uses
The cannabinoid THC-A is similar to the dominant cannabinoid of cannabis known as Delta 9 THC, but it is non-intoxicating until it is heated up to approximately 315°F in a process called decarboxylation. THC-A’s raw and inactivated form does not cause intoxication compared with its heated Delta 9 THC counterpart, which is why THC-A is all the rage with individuals who desire the benefits of cannabis without the feeling of being high.
THC-A in the Market: Availability and Forms
Raw cannabis juices, tinctures and some topical products, of which there exists a veritable cottage industry geared towards the health-conscious and the therapeutics-but-no-high crowd, are all made with THC-A. It’s common in what’s known as ‘live’ cannabis products – a focus in the California industry aimed at getting people to consume the freshest, most natural product possible, seeing as how years of developing strains and growing practices have diminished cannabis’ natural terpene and cannabinoid profiles, and sapping some of its nutritional value. An example is live resin, an oil made from un-dried (hence the ‘live’, or sometimes ‘fresh’ nomenclature) cannabis plants.
Delta 9 THC Products: Diversity and Popularity
It occurs naturally in all products made from dried flower containing Delta 9 THC, from traditional marijuana to edibles, oils and concentrates. This psychoactive cannabinoid may be quite great for both the mind and the body, and methods of taking Delta 9 THC vary wildly in terms of duration and intensity. When compared with smoking or vaping, edibles containing Delta 9 THC deliver a longer and more intensive high.
THCa vs Delta 9-THC
Is Hemp-Derived THC Legal?
Legality of THCA and Delta 9 THC depend on location; but ‘Hemp with a tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) level of 0.3% or less on a dry weight basis is not a controlled substance in the United States. THCA often also falls into a legal grey area since it is not psychoactive until it is decarboxylated. Make sure you’re following local laws regarding these compounds, as well.
Let’s look a little deeper at the subtlety of THCA and Delta 9 THC – how they could be good for you, what the science says about how they change, and what it means for the cannabis industry.
The Science of Decarboxylation: From THCA to Delta 9 THC
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group from THCA, transforming it into Delta 9 THC. This is due to decarboxylation – the loss of a carboxyl group. In the case of THCA, it becomes the psychoactive compound we know. It’s not just another chain-breaking carbon: it’s the psychotropic Richter scale. Decarboxylation no longer leads to the happy place of the hippie – it transports him or her to the land of altered states. When heat is applied to cannabis – whether it be by smoking, vaping, or cooking – THCA loses a carbon dioxide molecule. This changes it into Delta 9 THC.
Understanding the Process:
- Heat: Most commonly, decarboxylation is achieved using heat. When cannabis is burnt – that is, when it is smoked or vaporized – the heat is sufficient to convert THCA to Delta 9 THC.
- Sun and time: THCA will also convert to Delta 9 THC over time, and especially with exposure to sunlight. This is because UV light is very powerful radiation, meaning that its energy is very high. But this process is much slower and less efficient than heat-induced decarboxylation.
• Chemical Changes: This is the part of the process that actually changes the molecular shape of the original compound, and ushers it into the body’s endocannabinoid system, where psychoactive effects can ensue.
Their Role in the Cannabis Industry
THCA and Delta 9 THC play significant roles in the evolving cannabis industry:
- Product Diversity: In addition to the sheer number of products, there are flower, edibles, concentrates, and vapes, plus everything in between, featuring THCA and Delta 9 THC.
- Medical Research: Ongoing research
The step from THCA to Delta 9 THC suggests that the therapeutic landscape for medical cannabis could expand beyond current boundaries with new applications for specific health conditions. This work needs to be done.
- Legal and regulatory impact: If THCA is a different, distinct legal entity from Delta 9 THC, then cannabis businesses would likely operate under different legal frameworks, and the way the industry evolves would be vastly different today than it is – depending on the legal status of THCA – as laws change and the cannabis industry continues to be created in real time by those laws. Products that are subject to limits imposed by those laws will necessarily be products that consumers demand.
Consumer Education and Safety
With the growing interest in cannabis and its derivatives, consumer education has become paramount:
- Informed choices: Differentiating THCA from Delta 9 THC gives people alike an informed choice about their cannabis consumption, whether it be for medicinal or recreational purposes.
- Safety and Quality Control: Since the market grows, the safety and quality controls for the cannabis products that contain THCA and Delta 9 THC become even more critical. Consumers should buy only from credible sources with a publicly available laboratory testing and quality assurance.
Future Directions and Research
The future of THCA and Delta 9 THC is tied to ongoing research and industry innovation. Delta 9 THC and THCA are part of the cannabis conduit: two parts of one configuration. One affects emotions, one affects the mind. Industrial innovation, driven by new research, will transform our knowledge of molecules.
- Extraction: New and highly potent extracts and distillates of unheard-of purity are being created through advanced extraction and processing technologies that enable extremely precise dosing and effect.
- Clinical trials and studies: Over time, more clinical trials and studies will be conducted into THCA and its cancer-fighting property, particularly relating to the chemotherapeutic agent Delta 9 THC, further enhancing its therapeutic uses and potentially leading to new forms of treatment and therapies.
- Shifting consumer preferences: As consumer interests evolve, the cannabis industry will take cues, maintaining many of the product categories that we already have while innovating more varieties, including recreational offerings of Delta 9 THC and wellness-focused THCA products.
Final Thoughts about D9 vs THC-A
THCA and Delta 9 THC are two very different aspects of the cannabis plant, with their own distinct properties and benefits. They are projected to help drive the future of cannabis consumption, medicinal treatment and legal regulation as the cannabis industry continues to evolve. As cannabis laws change for the better, and its benefits become more widely understood among medical professionals and the general public, everyone could benefit. Everyone wants to know what makes the cannabis plant tick. Particularly those who want to use it recreationally or medicinally. For those suffering from a range of chronic illnesses, it can bring about much-needed relief, while for others it can simply be very enjoyable. Understanding the differences between THCA and Delta 9 THC could hold the key to the future of cannabis consumption – at least part of it. While they are both products of the same plant, they have very different effects, different legal statuses and a range of different benefits. The more we learn about these compounds, the more we will know.
THCa, by itself, isn’t known to cause intoxication or provide any euphoric or psychoactive high – eating THCa raw or even consuming gummies made from it won’t give you any kind of high, but you will come up positive on a drug test and could possibly even fail it.
Yes, if you use THCA products, you will still fail any urine drug test administered for THC; but that’s because both THC and THCA metabolise into the same metabolite in the body, codified by researchers of cannabinoids as COOH-THC. This is what we call the metabolite of THC, the one that’s tested for in all THC drug tests. THCA won’t get you high by itself, though once heat is applied to THCA, it ages into THC and can then show up on a drug test.
Delta-9 THC is the ‘psychoactive’ variety, formed by heating THCA, cannabis’s naturally occurring form of THC. THCA is not pyschoactive; you’d have to either smoke or cook it to convert it to psychoactive THC.
THCa is not intoxicating or psychoactive by itself. A person won’t get high from eating raw THCa or eating gummies made from it. (They will probably test positive, though, and it might lead to a failed drug test.) By itself, and with the high blunted by THCa, complications arise – nausea, indigestion or upset stomach, skin rashes, itching or chest tightness and other respiratory symptoms, or unwanted drug interactions with prescription medication. But any time THCa is cooked, heated or vaped it will turn it into the psychoactive drug THC.
- Short-Term Side Effects of Heating/Smoking THCa:
- Euphoria and relaxation
- Altered perception
- Impaired memory and cognition
- Dry mouth and increased thirst
- Bloodshot eyes
- Increased heart rate
- Anxiety and paranoia







