5 Terpenes You Should Know

Sara S.
Simple Leaf Staff
Exploring β-Pinene, β-Caryophyllene, Limonene, Humulene, and Myrcene Terpenes
Terpenes are a fascinating group of organic compounds that are found in various plants, including cannabis. These aromatic molecules not only contribute to the distinctive scents and flavors of different strains but also offer a wide range of potential health benefits. In this article, we will delve into the world of terpenes, focusing on five remarkable compounds: β-Pinene, β-Caryophyllene, Limonene, Humulene, and Myrcene. Get ready to embark on an aromatic journey that combines science, nature, and the wonders of these extraordinary terpenes.
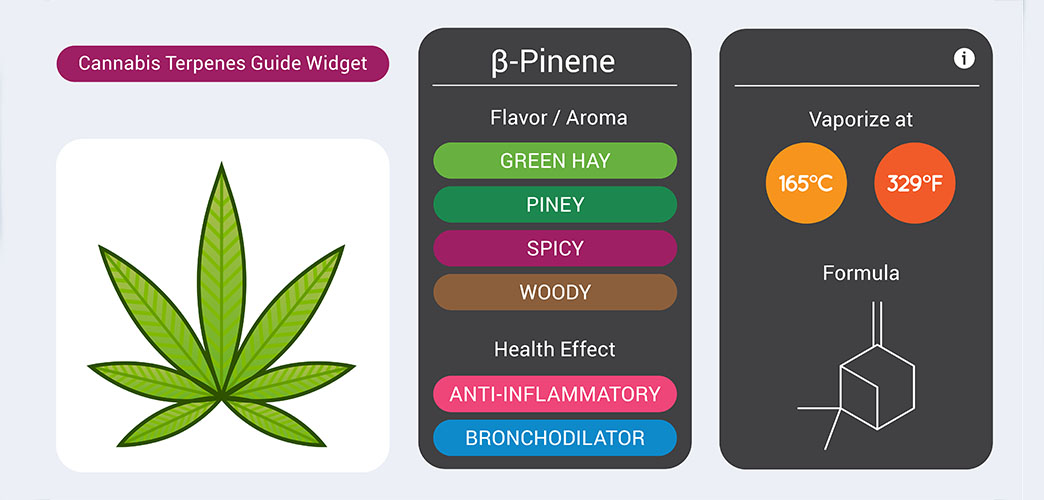
1. β-Pinene: The Uplifting Powerhouse
β-Pinene is one of the most prevalent terpenes found in nature, and it exudes a delightful aroma reminiscent of fresh pine needles. Besides contributing to the forest-like scent, this terpene holds tremendous therapeutic potential. Research suggests that β-pinene may possess anti-inflammatory properties, aid in respiratory health, and even enhance focus and memory. Its invigorating nature makes it a popular choice for individuals seeking an uplifting experience.
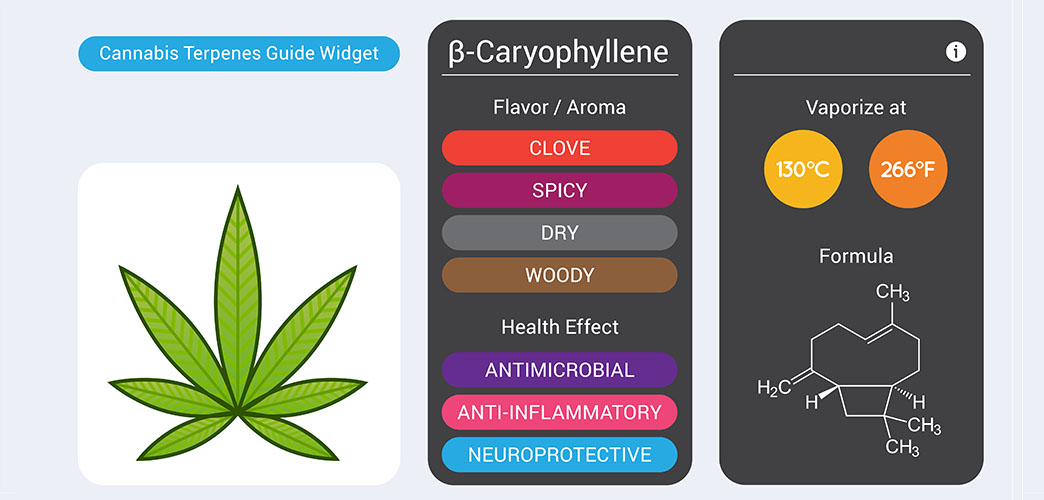
2. β-Caryophyllene: The Spicy Protector
β-Caryophyllene is a spicy terpene that is commonly found in black pepper, cloves, hops, black pepper, and cannabis. What sets it apart is its ability to interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, specifically targeting CB2 receptors. This interaction may result in anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. Additionally, β-caryophyllene exhibits the potential in supporting gastrointestinal health, reducing anxiety, and combating oxidative stress.
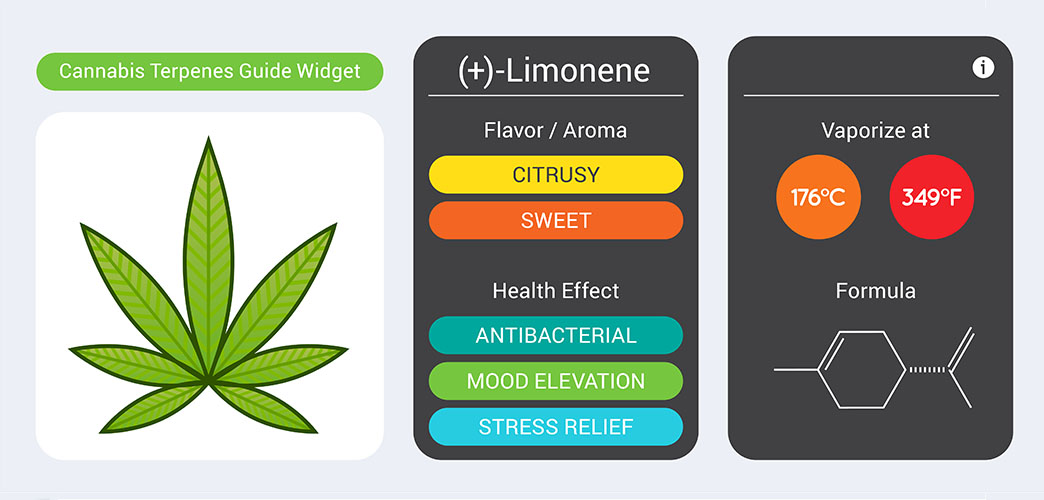
3. Limonene: The Zesty Energizer
As the name suggests, Limonene is responsible for the zesty, citrusy aroma found in fruits like lemons and oranges. This terpene has gained attention for its potential mood-enhancing properties, as it is believed to promote feelings of relaxation and reduce stress. Limonene may also possess antibacterial and antifungal properties, making it a valuable asset for supporting overall wellness.
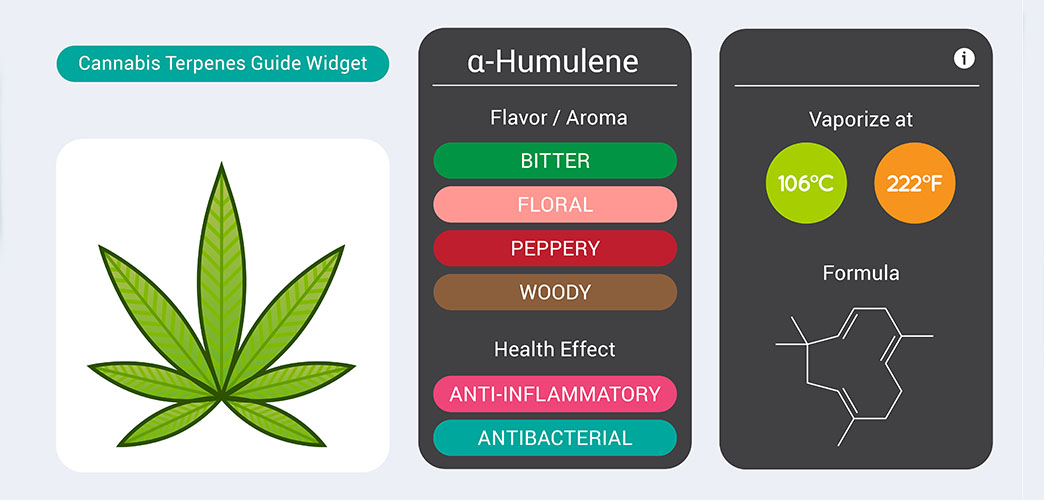
4. Humulene: The Earthy Healer
Humulene is a terpene that emanates an earthy, woody scent and is commonly found in ginseng, hops, basil, and cannabis. This unique terpene exhibits anti-inflammatory properties and has been studied for its potential in reducing pain and inflammation. Moreover, humulene may aid in weight management by acting as an appetite suppressant. Its multifaceted nature makes it an intriguing addition to the terpene family.
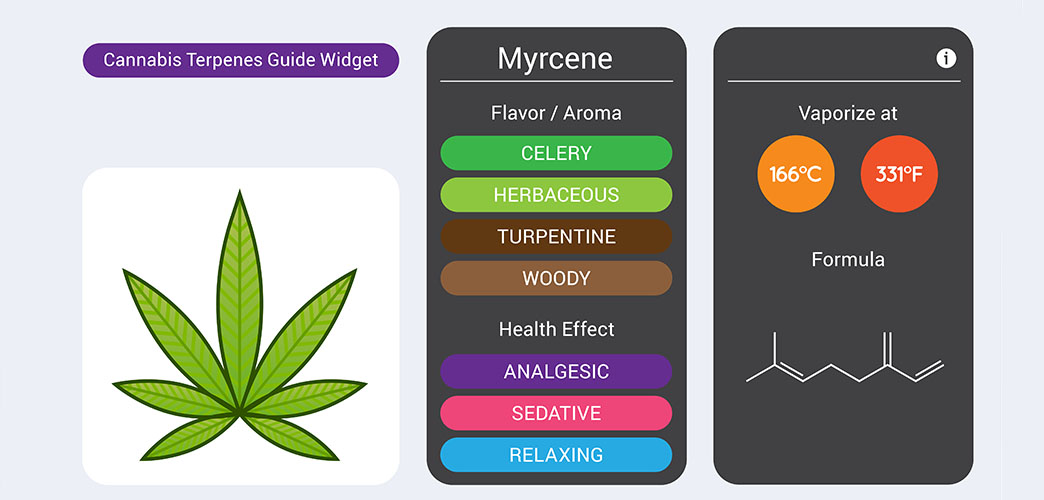
5. Myrcene: The Relaxing Companion
Myrcene is a terpene renowned for its tranquilizing and sedative effects, often associated with Indica strains of cannabis. This compound carries a herbal aroma and is also present in high quantities in plants like mangoes and hops. Research suggests that myrcene may possess analgesic properties, making it beneficial for individuals seeking pain relief. Additionally, this terpene may aid in sleep quality, relaxation, and stress reduction.
5 Terpenes You Should Know
The world of terpenes is a captivating realm that reveals the wonders of nature’s aromatic diversity. From the uplifting powers of β-pinene to the soothing effects of myrcene, each terpene presents a unique set of characteristics and potential benefits. It is essential to remember that terpenes work synergistically with other compounds, including cannabinoids, to produce the entourage effect. This phenomenon emphasizes the importance of understanding the intricate relationship between terpenes and cannabis.
By exploring the terpenes β-Pinene, β-Caryophyllene, Limonene, Humulene, and Myrcene, we have unlocked a treasure trove of aromas and therapeutic potential. Whether you seek a mood boost, pain relief, or stress reduction, these terpenes offer a fascinating pathway to holistic well-being.
Sources:
- Russo, E. B. (2011). Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid-terpenoid entourage effects. British Journal of Pharmacology, 163(7), 1344–1364.
- Jirovetz, L., Buchbauer, G., Denkova, Z., Slavchev, A., Stoyanova, A., & Schmidt, E. (2006). Chemical Composition, Antifungal and Antioxidant Properties of Yarrow (Achillea millefolium L.) Essential Oil. Journal of Essential Oil Research, 18(3), 341–343.
- Legault, J., Dahl, W., Debiton, E., Pichette, A., & Madelmont, J.-C. (2003). Antitumor Activity of Balsam Fir Oil: Production of Reactive Oxygen Species Induced by α-Humulene as Possible Mechanism of Action. Planta Medica, 69(5), 402–407.
- Nair, J. J., van Staden, J., & Verschaeve, L. (2015). Aromatic Plants: A Potential Source of Lead Compounds for Drug Discovery. Molecules, 20(10), 19520–19555.
- Izzo, A. A., & Capasso, R. (2001). Herbal Medicine: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. In Drug Discovery Today, 6(8), 45–46.